INTRODUCTION
JavaScript (js) is a light-weight object-oriented programming language which is used by several websites
for scripting the webpages. It is an interpreted, full-fledged programming language that enables dynamic
interactivity on websites when applied to an HTML document. It was introduced in the year 1995 for
adding programs to the webpages in the Netscape Navigator browser. Since then, it has been adopted by
all other graphical web browsers. With JavaScript, users can build modern web applications to interact
directly without reloading the page every time. The traditional website uses js to provide several forms
of interactivity and simplicity.
Although, JavaScript has no connectivity with Java programming language. The name was suggested and
provided in the times when Java was gaining popularity in the market. In addition to web browsers,
databases such as CouchDB and MongoDB uses JavaScript as their scripting and query language.
VARIABLE
A JavaScript variable is simply a name of storage location. There are two types of variables in
JavaScript : local variable and global variable.

OPERATORS
What is an Operator?
Let us take a simple expression 4 + 5 is equal to 9. Here 4 and 5 are called operands and ‘+’ is
called the operator. JavaScript supports the following types of operators.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison (Relational) Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Special Operators
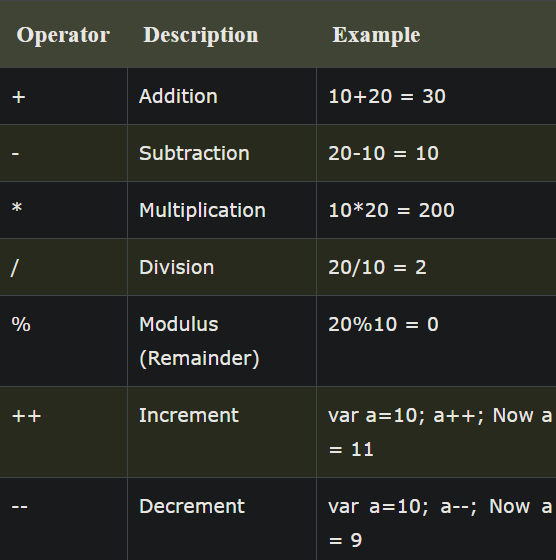
ARITHMATIC OPERATORS
DATA TYPES
JavaScript provides different data types to hold different types of values. There are two types of
data types in JavaScript.
- Primitive data type
- Non-primitive (reference) data type
JavaScript is a dynamic type language, means you don't need to specify type of the variable because it is
dynamically used by JavaScript engine. You need to use var here to specify the data type. It can hold
any type of values such as numbers, strings etc.
