INTRODUCTION
Cascading Style Sheets, fondly referred to as CSS, is a simple design language intended to simplify the
process of making web pages presentable.
CSS handles the look and feel part of a web page. Using CSS, you can control the color of the text, the
style of fonts, the spacing between paragraphs, how columns are sized and laid out, what background
images or colors are used, layout designs,variations in display for different devices and screen sizes
as well as a variety of other effects.
CSS is easy to learn and understand but it provides powerful control over the presentation of an HTML
document. Most commonly, CSS is combined with the markup languages HTML or XHTML.
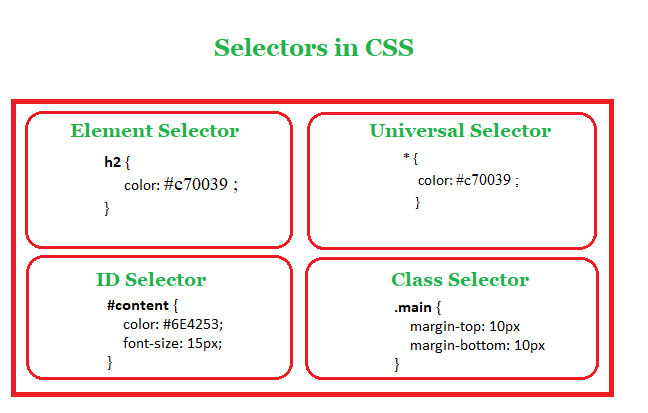
SELECTORS
CSS selectors are used to select the content you want to style. Selectors are the part of CSS rule set.
CSS selectors select HTML elements according to its id, class, type, attribute etc.
There are several different types of selectors in CSS.
- CSS Element Selector
- CSS Id Selector
- CSS Id Selector
- CSS Universal Selector
- CSS group Selector
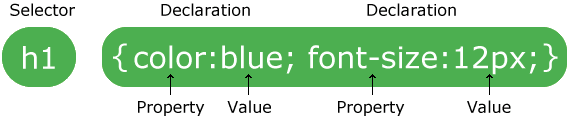
SYNTAX
A CSS comprises of style rules that are interpreted by the browser and then applied to the corresponding
elements in your document. A style rule is made of three parts −
- Selector− A selector is an HTML tag at which a style will be applied. This could be any tag
like h1 or table tag etc.
- Property− A property is a type of attribute of HTML tag. Put simply, all the HTML attributes
are converted into CSS properties. They could be color, border etc.
- Value− Values are assigned to properties. For example, color property can have value either
red or #F1F1F1 etc.
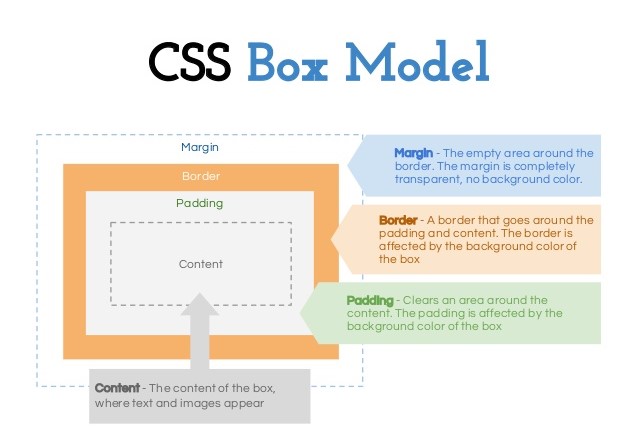
BOX-MODEL
CSS box model is a container which contains multiple properties including borders, margin, padding and
the content itself. It is used to create the design and layout of web pages. It can be used as a toolkit
for customizing the layout of different elements. The web browser renders every element as a rectangular
box according to the CSS box model.